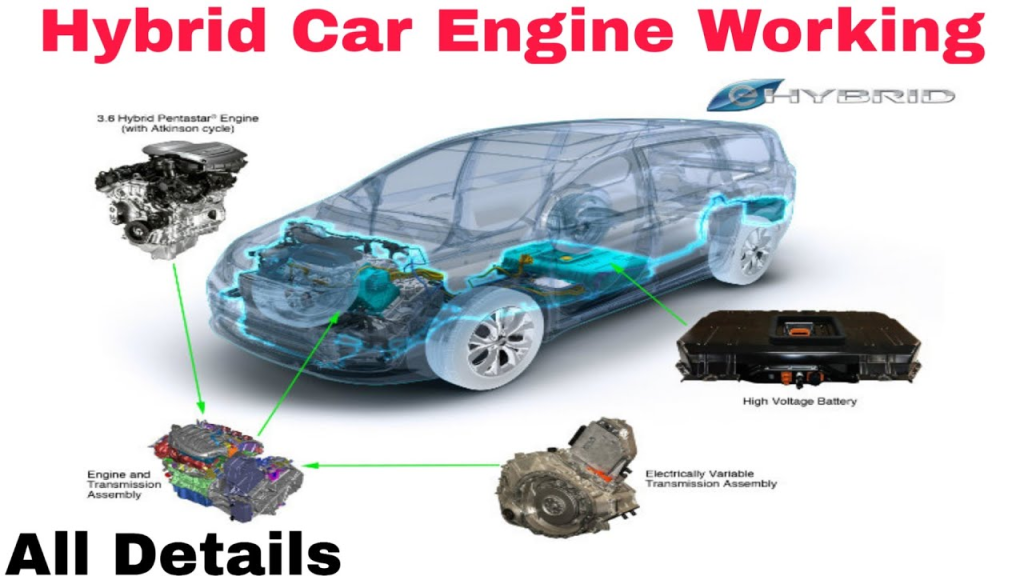
A hybrid car is a vehicle that combines two or more power sources to move the vehicle. Most commonly, a hybrid car combines a traditional gasoline or diesel engine with an electric motor and battery pack. The gasoline or diesel engine is used to propel the car forward and to charge the battery pack when it is running low, while the electric motor provides additional power to the car and captures energy during braking. The battery pack stores the captured energy from the electric motor and provides power to the car’s accessories. A hybrid car’s computer system controls how power is delivered to the wheels, based on driving conditions, and some models can be charged by plugging them into an electrical outlet. Overall, the hybrid car’s design and technology aim to reduce emissions and improve fuel economy, while still providing the performance and range that drivers need.
How does a hybrid car work?
A hybrid car works by combining two or more power sources to move the vehicle. Typically, a hybrid car combines a traditional gasoline or diesel engine with an electric motor and a battery pack. Here is a more detailed explanation of how a hybrid car works:
- Gasoline or diesel engine: The car is powered by a gasoline or diesel engine, just like a conventional car. The engine is used to propel the car forward and to charge the battery pack when it is running low.
- Electric motor: The car also has an electric motor that works in conjunction with the gasoline or diesel engine. The electric motor provides additional power to the car, helping it to accelerate and climb hills more efficiently. It also works to capture energy during braking, which is stored in the battery pack.
- Battery pack: The battery pack is used to store energy captured by the electric motor and to provide power to the car’s accessories, such as the air conditioning and radio. The battery pack is recharged by both the gasoline or diesel engine and the electric motor.
- Regenerative braking: When the driver applies the brakes, the electric motor works as a generator, capturing energy that would normally be lost as heat through the brakes. This energy is then stored in the battery pack and used to power the car later.
- Computer system: The car’s computer system controls how power is delivered to the wheels, based on driving conditions and other factors. For example, the electric motor might be used to power the car at low speeds, while the gasoline or diesel engine takes over at higher speeds or when more power is needed.
- Plug-in hybrids: Some hybrid cars are designed to be plug-in hybrids, which means they can be charged by plugging them into an electrical outlet. This allows the car to run on electric power alone for a certain distance, before the gasoline or diesel engine kicks in.
Overall, the goal of a hybrid car is to reduce emissions and improve fuel economy, while still providing the performance and range that drivers need. By combining a gasoline or diesel engine with an electric motor and battery pack, hybrid cars are able to offer the best of both worlds in terms of efficiency and performance.
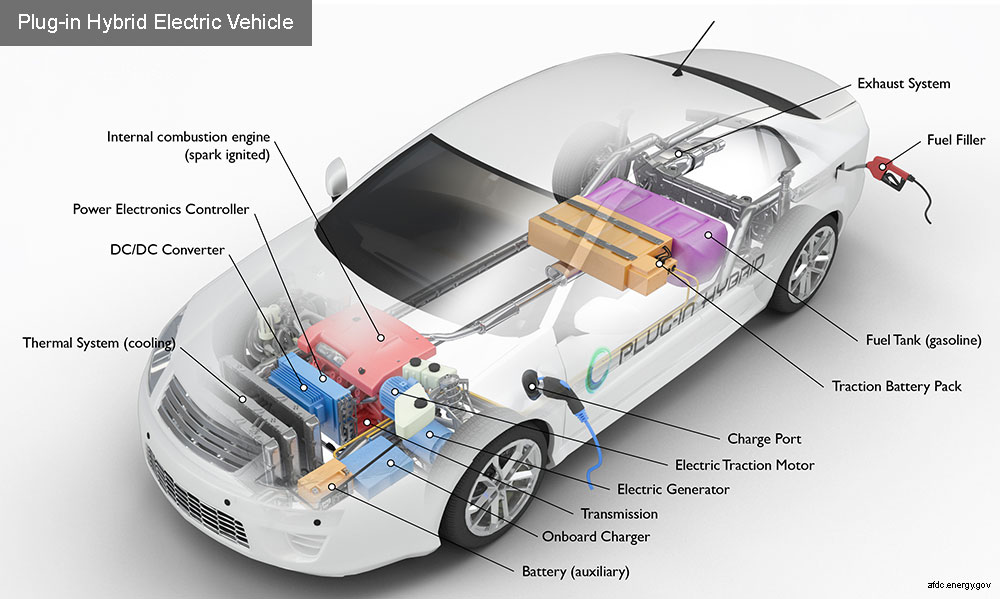
Step-by-step explanation of how a hybrid car works
- The car is powered by a gasoline engine, just like a conventional car. The engine propels the car forward and charges the battery pack when it’s running low.
- The car also has an electric motor that works in conjunction with the gasoline engine. The electric motor provides additional power to the car, helping it to accelerate and climb hills more efficiently.
- The car has a battery pack that stores energy captured by the electric motor and provides power to the car’s accessories, such as air conditioning and radio.
- When the driver applies the brakes, the electric motor works as a generator, capturing energy that would normally be lost as heat through the brakes. This energy is then stored in the battery pack and used to power the car later.
- The car’s computer system controls how power is delivered to the wheels, based on driving conditions and other factors. For example, the electric motor might be used to power the car at low speeds, while the gasoline engine takes over at higher speeds or when more power is needed.
- Some hybrid cars are designed to be plug-in hybrids, which means they can be charged by plugging them into an electrical outlet. This allows the car to run on electric power alone for a certain distance, before the gasoline engine kicks in.
Some examples of hybrid cars
Here are some examples of hybrid cars:
- Toyota Prius: The Prius is one of the most well-known hybrid cars on the market. It uses a combination of a gasoline engine and an electric motor to provide power, and it has a regenerative braking system to capture energy and recharge the battery. The Prius gets an estimated 54 miles per gallon in combined city and highway driving.
- Honda Accord Hybrid: The Accord Hybrid is a midsize sedan that uses a two-motor hybrid system to provide power. The car can operate in electric-only mode for short distances, and it has a regenerative braking system to recharge the battery. The Accord Hybrid gets an estimated 48 miles per gallon in combined city and highway driving.
- Ford Fusion Hybrid: The Fusion Hybrid is a midsize sedan that uses a combination of a gasoline engine and an electric motor to provide power. It has a regenerative braking system to capture energy and recharge the battery, and it can operate in electric-only mode at low speeds. The Fusion Hybrid gets an estimated 42 miles per gallon in combined city and highway driving.
- Chevrolet Volt: The Volt is a plug-in hybrid that can run on electric power alone for up to 53 miles before the gasoline engine kicks in. The car has a regenerative braking system to recharge the battery, and it can be charged by plugging it into an electrical outlet. The Volt gets an estimated 42 miles per gallon in combined city and highway driving.
These are just a few examples of the many hybrid cars on the market today. Each car has its own unique combination of gasoline engine, electric motor, and battery pack, as well as different features like regenerative braking and plug-in capability.
Conclusion
In conclusion, hybrid cars work by using a combination of electric and gasoline power sources. The electric motor is used to power the car at lower speeds and during acceleration, while the gasoline engine kicks in to provide power during high-speed driving or when the battery is low. The battery pack is charged by regenerative braking and the gasoline engine, and some hybrids can also be charged through an external power source. This unique combination of power sources results in higher fuel efficiency, lower emissions, and reduced reliance on gasoline. Additionally, some hybrids have features like start-stop systems and idle-off technology that further improve fuel efficiency. Overall, hybrid cars offer a more sustainable and environmentally friendly option for those who want to reduce their carbon footprint while still enjoying the benefits of a traditional gasoline-powered car.
