As the demand for eco-friendly and fuel-efficient cars continues to grow, hybrid cars have become increasingly popular. Hybrid cars come in various types and designs, with parallel and series hybrids being the most common. The main difference between these two types of hybrid cars is the way their engines and electric motors work together. Understanding the differences between parallel and series hybrids can help potential buyers make an informed decision when choosing a hybrid car. In this blog post, we will explore the differences between parallel and series hybrids, and their unique features and benefits.
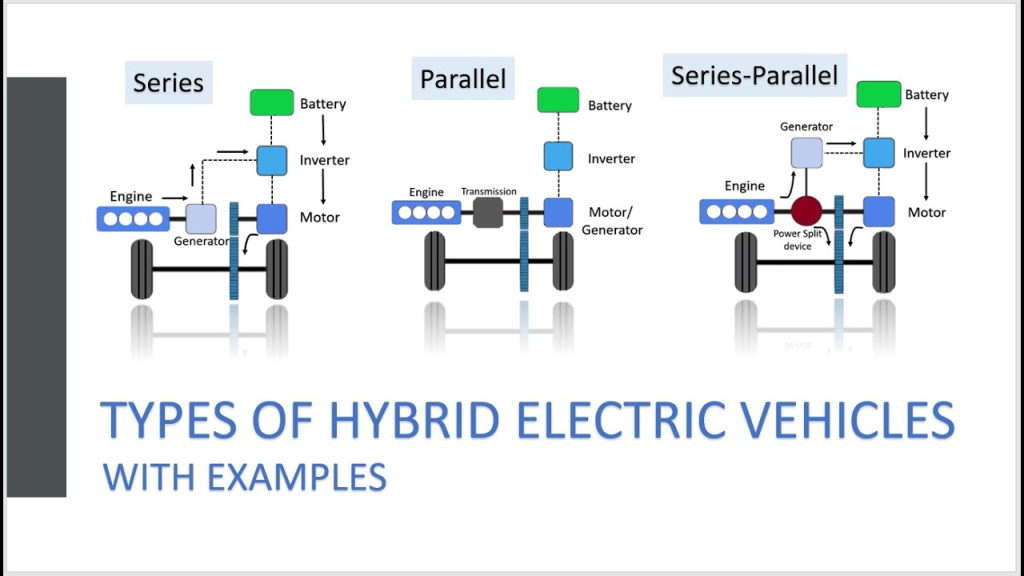
What is the difference between a parallel hybrid and a series hybrid?
Below are some difference between a parallel hybrid and a series hybrid
Parallel Hybrid:
- The gasoline engine and electric motor work together to drive the wheels.
- The electric motor acts as a power boost to the gasoline engine.
- The electric motor can power the car on its own for short distances.
- The battery can be recharged through regenerative braking and while the gasoline engine is running.
- The gasoline engine is the primary source of power for the car.
- The electric motor is used to supplement the gasoline engine, especially during acceleration.
- The gasoline engine turns off when the car is stopped.
- The electric motor can start the car moving from a stop.
- The car switches between gasoline and electric power depending on driving conditions.
- The car can achieve better fuel efficiency in stop-and-go city driving.
- Examples of parallel hybrid cars include Toyota Prius, Honda Insight, and Ford Fusion Hybrid.
- Parallel hybrids are more common than series hybrids.
- Parallel hybrids have a simpler and more compact design.
- Parallel hybrids are generally less expensive than series hybrids.
- Parallel hybrids can operate at higher speeds using gasoline engine power.
- The electric motor in parallel hybrids has less torque than in series hybrids.
- Parallel hybrids have a smaller battery than series hybrids.
- The battery in parallel hybrids is located under the rear seat or in the trunk.
- The gasoline engine in parallel hybrids is smaller than in non-hybrid cars.
- Parallel hybrids offer smoother and more seamless acceleration.
- Parallel hybrids emit less pollution than non-hybrid cars.
- Parallel hybrids require less maintenance than non-hybrid cars.
- Parallel hybrids have a longer driving range than pure electric cars.
- Parallel hybrids are a good choice for drivers who want fuel efficiency without sacrificing performance.
- Parallel hybrids are a good choice for drivers who do mostly city driving.
Series Hybrid:
- The gasoline engine does not drive the wheels directly.
- The gasoline engine powers a generator that produces electricity to power the electric motor.
- The electric motor drives the wheels.
- The battery can be recharged through regenerative braking and while the gasoline engine is running.
- The electric motor is the primary source of power for the car.
- The gasoline engine is used to generate electricity, not to power the car directly.
- The gasoline engine always runs at the most efficient speed for generating electricity.
- The electric motor can power the car on its own for short distances.
- The car can achieve better fuel efficiency on highways and at steady speeds.
- Examples of series hybrid cars include Chevrolet Volt and BMW i3 with range extender.
- Series hybrids are less common than parallel hybrids.
- Series hybrids have a more complex and larger design.
- Series hybrids are generally more expensive than parallel hybrids.
- Series hybrids can operate at lower speeds using electric motor power.
- The electric motor in series hybrids has more torque than in parallel hybrids.
- Series hybrids have a larger battery than parallel hybrids.
- The battery in series hybrids is located in the center of the car.
- The gasoline engine in series hybrids is larger than in parallel hybrids.
- Series hybrids offer quieter and smoother operation.
- Series hybrids emit less pollution than non-hybrid cars.
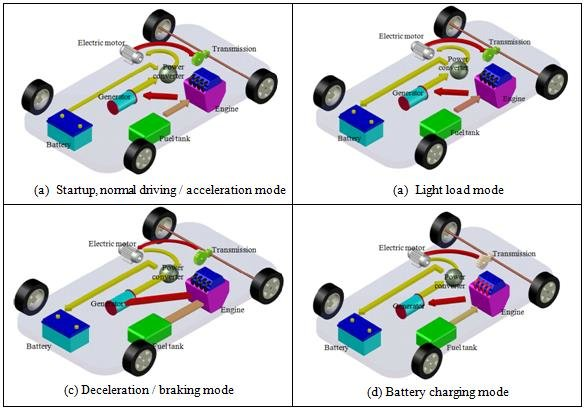
Some Examples how parallel hybrid is difference from a series hybrid
Below are Some examples of the differences between the two types of hybrids:
- Power delivery: In a parallel hybrid, both the engine and the electric motor work together to provide power to the wheels. In contrast, in a series hybrid, the engine only generates electricity to power the electric motor, which then drives the wheels.
- Electric-only mode: Some parallel hybrids can operate in electric-only mode at low speeds, while series hybrids cannot.
- Battery size: Series hybrids tend to have larger batteries than parallel hybrids, as they rely more heavily on electric power.
- Efficiency: In general, series hybrids tend to be more fuel-efficient than parallel hybrids due to their greater reliance on electric power.
- Driving experience: Parallel hybrids tend to provide a more seamless driving experience, as the engine and electric motor work together more seamlessly. Series hybrids may have a more noticeable transition between gas and electric power.
- Regenerative braking: Both types of hybrids use regenerative braking to recharge the battery, but the system works slightly differently in each. In a parallel hybrid, the electric motor helps slow the car down, while in a series hybrid, the electric motor acts as a generator to recharge the battery.
- Weight distribution: Parallel hybrids tend to have a more even weight distribution between the front and rear of the car, while series hybrids may be front-heavy due to the placement of the engine.
- Cost: Series hybrids tend to be more expensive than parallel hybrids, due to the larger battery and more complex powertrain.
- Acceleration: Parallel hybrids may provide better acceleration than series hybrids, as both the engine and electric motor can work together to deliver more power.
- Driving range: In general, series hybrids tend to have a longer electric-only driving range than parallel hybrids, as they rely more heavily on electric power.
Some facts about parallel hybrid and a series hybrid car
Below are some facts about parallel hybrid and a series hybrid car
- In a parallel hybrid, both the electric motor and internal combustion engine are mechanically connected to the transmission, while in a series hybrid, the internal combustion engine is only used to charge the battery and is not mechanically connected to the transmission.
- Parallel hybrids tend to be more fuel-efficient in city driving, where frequent starts and stops are required, while series hybrids are more fuel-efficient in highway driving.
- Parallel hybrids have a larger battery than series hybrids, which allows them to drive further on electric power alone.
- Series hybrids are typically more expensive than parallel hybrids because they require a larger battery and more complex drivetrain.
- Parallel hybrids can provide more power and better acceleration than series hybrids because both the electric motor and internal combustion engine can work together to deliver power to the wheels.
- In a parallel hybrid, the internal combustion engine can shut off while the car is idling, which saves fuel and reduces emissions.
- Series hybrids tend to have better regenerative braking systems because the electric motor is solely responsible for slowing down the car and capturing energy that would otherwise be lost as heat.
- Parallel hybrids tend to have a smoother and more seamless transition between electric and gasoline power, while series hybrids may have a more noticeable switch between the two.
- Series hybrids are typically quieter than parallel hybrids because the internal combustion engine is only used to charge the battery and does not power the wheels directly.
- In a parallel hybrid, the internal combustion engine can be used to recharge the battery while driving, which extends the range of the electric motor.
- Series hybrids have a simpler and more reliable drivetrain because the electric motor is responsible for all the power delivered to the wheels.
- Parallel hybrids tend to have a shorter lifespan for the battery because it is used more frequently and discharged to a greater degree.
- Series hybrids tend to have a longer lifespan for the battery because it is not used as frequently and is discharged to a lesser degree.
- Parallel hybrids require a larger and more powerful starter motor to start the internal combustion engine, while series hybrids do not have a starter motor at all.
- In a parallel hybrid, the internal combustion engine can be used to heat the interior of the car, while in a series hybrid, an electric heater is used.
- Series hybrids can provide more consistent and predictable fuel economy because the internal combustion engine is only used to charge the battery and is not affected by driving conditions as much as in a parallel hybrid.
- Parallel hybrids can provide more power to the wheels because the electric motor and internal combustion engine can work together to deliver power when needed.
- Series hybrids can operate more efficiently at low speeds because the electric motor is more efficient than an internal combustion engine at low speeds.
- Parallel hybrids can have a more complicated and difficult-to-maintain drivetrain because of the mechanical connection between the electric motor, internal combustion engine, and transmission.
- Series hybrids can have a more simplified and easier-to-maintain drivetrain because of the separation between the electric motor and internal combustion engine.
Conclusion
In conclusion, both parallel and series hybrid cars offer advantages in terms of fuel efficiency and reduced emissions. The main difference between the two is how the electric motor and the gasoline engine work together to propel the vehicle. Parallel hybrids use both the gasoline engine and electric motor to drive the wheels, while series hybrids use the electric motor to drive the wheels, with the gasoline engine acting as a generator to recharge the battery. The choice between the two depends on the specific needs and preferences of the driver. Both types of hybrids have their own unique benefits and drawbacks, and it’s important for consumers to consider these factors when choosing the right hybrid car for them.
